The 3rd International Workshop on "XYLELLA FASTIDIOSA: DIAGNOSIS, CONTROL AND MANAGEMENT MEASURES” will take place at the National Agricultural Research Center (NARC – MoA), Jenin, Palestine, from 21 to 23 June 2022.
Invitation-3rd-International-Workshop-Xf-_-PalestineDownload
Program_X-ylella-workshop_Palestine-13-06-closingDownload
Read More
Olive quick decline syndrome (OQDS), which is caused by Xylella fastidiosa, poses a severe threat to the agriculture of Mediterranean countries and causes severe damage to the olive trees in Italy. Since no effective control measures are currently available, the objective of this study was the screening of antagonistic bacteria that are potentially deployable as biocontrol agents against X. fastidiosa. Therefore, two approaches were used, i.e., the evaluation of the antagonistic activity of (i)...
Read More
Morocco belongs to the countries ranked at a high-risk level for entry, establishment, and spread of Xylella fastidiosa, which has recently re-emerged as a plant pathogen of global impor- tance causing olive quick decline syndrome (OQDS).
Symptomatic infection by X. fastidiosa leads to devastating diseases and important economic losses. To prevent such losses and damages, countries without current outbreaks like Morocco need to first understand their host plant responses to X. fastidiosa.
...
Read More
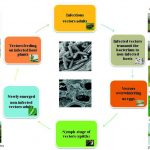
The Philaenus spumarius L. (Hemiptera Aphrophoridae) is a xylem-sap feeder vector that acquires Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca ST53 during feeding on infected plants. The bacterium is the plant pathogen responsible for olive quick decline syndrome that has decimated olive trees in Southern Italy.
Damage originates mainly from the insect vector attitude that multiplies the pathogen potentialities propagating Xf in time and space. The principal action to manage insect-borne pathogens and to ...
Read More
Since its outbreak in 2013 in Italy, the harmful bacterium Xylella fastidiosa has continued to spread throughout the Euro-Mediterranean basin and, more recently, in the Middle East region. Xylella fastidiosa subsp. fastidiosa is the causal agent of Pierce’s disease on grapevines.
At present, this alien subspecies has not been reported in Lebanon but if this biological invader was to spread with no cost-effective and sustainable management, it would put Lebanese vineyards at a certain level ...
Read More
Endophytes are symptomless fungal and/or bacterial microorganisms found in almost all living plant species. The symbiotic association with their host plants by colonizing the internal tissues has endowed them as a valuable tool to suppress diseases, stimulate growth, and promote stress resistance.
In this context, the study of culturable endophytes residing the sapwood of Apulian olives might be a promising control strategy for xylem colonizing pathogens as Xylella fastidiosa. To date, oliv...
Read More
November marks the 25th anniversary of the Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions (MSCA) programme that has funded the research of about 145,000 PhDs and postdocs in Europe and beyond, and equipped them with new knowledge and skills. Recipients discuss how the MSCA were a stepping stone to excelling in academia and industry.
For 25 years, the MSCA has been training researchers, many of whom have gone on to make great contributions to both the scientific community and society overall. Recip...
Read More
Since 2013, the olive landscapes have gradually degenerated due to the spread and establishment of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca (hereafter Xf) in Apulia, southern Italy. From 2013 to 2019, a total of approximately 54,000 hectares of olive orchards in the south of this region have been seriously damaged, and their restoration will progressively regenerate the economic, social, cultural and environmental nonmarket benefits. Since there is a willingness to restore the affected landscape in the ...
Read More
Morocco belongs to the countries ranked at a high-risk level for entry, establishment, and spread of Xylella fastidiosa, which has recently re-emerged as a plant pathogen of global importance causing olive quick decline syndrome (OQDS). Symptomatic infection by X. fastidiosa leads to devastating diseases and important economic losses. To prevent such losses and damages, countries without current outbreaks like Morocco need to first understand their host plant responses to X....
Read More
The meeting of XF-ACTORS, the EU Horizon 2020 research project devoted to this plant pathogenic bacterium, will precede the conference. The 3rd European conference on Xylella fastidiosa is organised by EFSA and XF-ACTORS with the active contribution of the major EU and transnational research initiatives tackling X. fastidiosa – BIOVEXO, CURE-XF, ERC MultiX, EUPHRESCO, EUROXANTH, and Life Resilience.
For more information: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/it/events/event/3rd...
Read More